The Manning lab is delineating the molecular wiring and functions of a signal transduction network that senses and responds to nutrients and other growth stimuli, is aberrantly regulated in a diverse set of human diseases, and plays an evolutionarily conserved role in aging. In normal cells, the PI3K-mTOR signaling network is exquisitely regulated by both cell intrinsic signals, in the form of nutrients and cellular stress, and exogenous signals from secreted growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. The Manning lab has found that these physiological signals are sensed in an integrated manner that assures that the pathway is spatially and temporally activated only under optimal local and systemic nutrient conditions. Several projects in the lab are aimed at defining regulatory mechanisms involving the TSC protein complex, which is a central, signal-integrating node within this vast network. Furthermore, negative feedback mechanisms are prevalent within the network and have a profound influence on the intensity and duration of signal propagation, as well as the response of the network to pharmacological interventions. The importance of a mechanistic understanding of this regulation is underscored by the fact that aberrant signaling within the network is a common feature of pathological states, including cancer, type-2 diabetes, and obesity.
Related Publications
Valvezan AJ, Manning BD. Molecular logic of mTORC1 signalling as a metabolic rheostat. Nat Metab. 2019 Mar;1(3):321-333. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0038-7. Epub 2019 Mar 4. PMID: 32694720
Hoxhaj G, Hughes-Hallett J, Timson RC, Ilagan E, Yuan M, Asara JM, Ben-Sahra I, Manning BD. The mTORC1 Signaling Network Senses Changes in Cellular Purine Nucleotide Levels. Cell Rep. 2017; 21(5):1331-1346. PMID: 29091770
Manning BD. Game of TOR – The Target of Rapamycin Rules Four Kingdoms. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377(13):1297-9. PMID: 28874074
Manning BD, Toker A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell. 2017; 169(3):381-405. PMID: 28431241
Howell JJ, Hellberg K, Turner M, Talbott G, Kolar MJ, Ross DS, Hoxhaj G, Saghatelian A, Shaw RJ, Manning BD. Metformin Inhibits Hepatic mTORC1 Signaling via Dose-Dependent Mechanisms Involving AMPK and the TSC Complex. Cell Metab. 2017; 25(2):463-471. PMID: 28089566
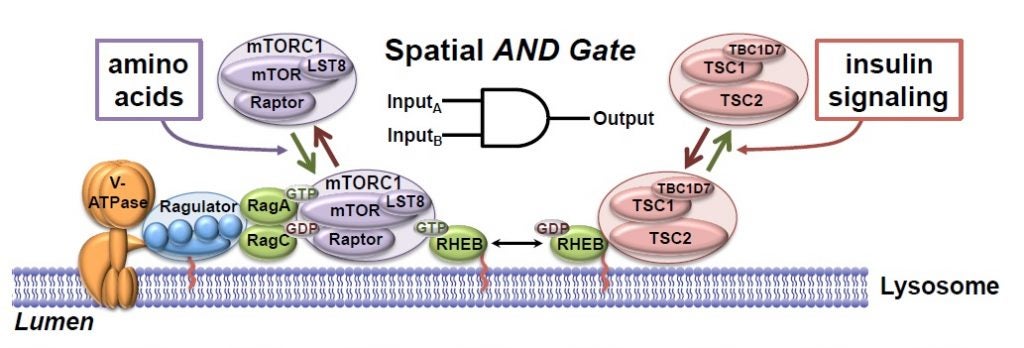
Menon S, Dibble CC, Talbott G, Hoxhaj G, Valvezan AJ, Takahashi H, Cantley LC, Manning BD. Spatial Control of the TSC Complex Integrates Insulin and Nutrient Regulation of mTORC1 at the Lysosome. Cell. 2014; 156(4):771-85. PMID: 24529379
Dibble CC, Manning BD. Signal intergration by mTORC1 coordinates nutrient input with biosynthetic output. Nat Cell Biol. 2013; 15(6):555-64. PMID: 23728461
Dibble CC, Elis W, Menon S, Qin W, Klekota J, Asara JM, Finan PM, Kwiatkowski DJ, Murphy LO, Manning BD. TBC1D7 is a third subunit of the TSC1-TSC2 complex upstream of mTORC1. Mol Cell. 2012; 47(4):535-46. PMID: 22795129
Dibble CC, Asara JM, and Manning BD. Characterization of Rictor phosphorylation sites reveals direct regulation of mTOR complex 2 by S6K1. Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 29(21):5657-70. PMID: 19720745
Huang J, Dibble CC, Matsuzaki M, and Manning BD. The TSC1-TSC2 complex is required for proper activation of mTOR complex 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2008; 28(12):4104-15. PMID: 18411301
Ozcan U, Ozcan L, Yilmaz E, Düvel K, Sahin M, Manning BD, and Hotamisligil GS. Loss of the tuberous sclerosis complex tumor suppressors triggers the unfolded protein response to regulate insulin signaling and apoptosis. Mol Cell. 2008; 29(5):541-51. PMID: 18342602
Huang J and Manning BD. The TSC1-TSC2 complex: a molecular switchboard controlling cell growth. Biochem J. 2008; 412(2):179-90. PMID: 18466115
Manning BD, Cantley LC. AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 2007; 129:1261-74. PMID:17604717
Zhang HH, Lipovsky AI, Dibble CC, Sahin M, Manning BD. S6K1 regulates GSK3 under conditions of mTOR-dependent feedback inhibition of Akt. Mol Cell. 2006; 24(2):185-97. PMID: 17052453
Manning BD, Tee AR, Logsdon MN, Blenis J, Cantley LC. Identification of the tuberous sclerosis complex-2 tumor suppressor gene product tuberin as a target of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/akt pathway. Mol Cell 2002; 10:151-62. PMID:12150915