Introduction In India, as in many low-income and middle-income countries, the private sector provides a large share of health care. Pharmacies represent a major share of private care, yet there are few studies on their role as healthcare providers. Our study examines: (1) What are the characteristics of and services provided by private pharmacies and how do these compare with other outpatient care providers? (2) What are the characteristics of…
Working Paper 8: A Guide to Health Reform: Eight Practical Steps
A Guide to Health Reform: Eight Practical Steps By Michael R. Reich, Paola Abril Campos, Anuska Kalita, Anya Levy Guyer, and Winnie Yip August 2023 A Guide to Health Reform: Eight Practical Steps instructs readers on how to navigate the complex challenges of doing health system reform. The Guide builds on the 2004 book Getting Health Reform Right: A Guide to Improving Performance and Equity (GHRR), which presents a framework…
Continue reading “Working Paper 8: A Guide to Health Reform: Eight Practical Steps”
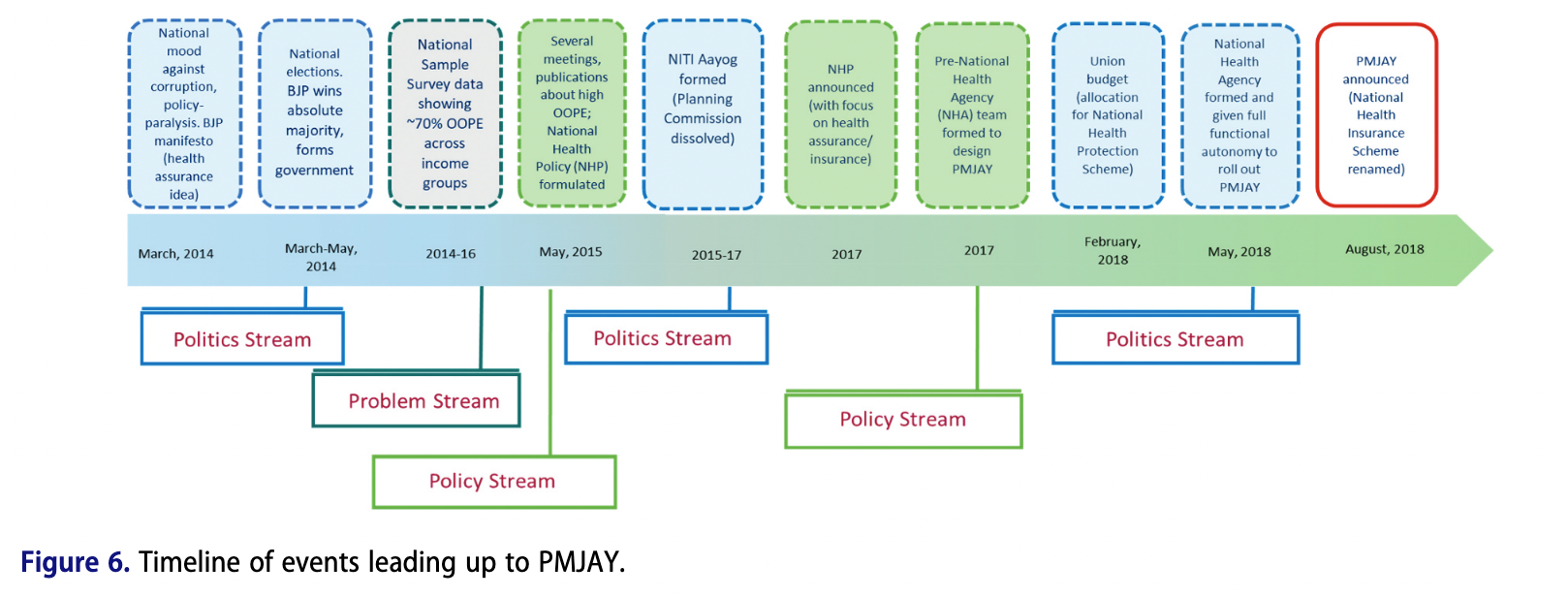
Publication: The Politics of Health Policy Agenda Setting in India: The Case of the PMJAY Program
Abstract In 2018, India’s Prime Minister announced a new health insurance program, Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY), aiming to cover over 500 million people. This paper seeks to document and explain the emergence of PMJAY on India’s political and policy agendas. We analyze media, election manifestos, legislative debates, and health budgets to compare PMJAY’s presence on India’s policy agenda to previous health programs. We then apply Kingdon’s Multiple Streams…
Working Paper 7: State-Level Health Systems Assessments in India Based on Publicly Available Data
State-Level Health Systems Assessments in India Based on Publicly Available Data By Bijetri Bose November 2022 India has engaged in several healthcare reforms at the national and state levels since the 2000s and has experienced significant improvements in many health outcomes of its people. Yet, the nation continues to face challenges in its health system that impedes the progress toward universal health coverage where all people have access to good…
Working Paper 6: China’s Internet Health Market
China’s Internet Health Market By Hongqiao Fu, Terence Cheng, Duo Xu, and Yuzhu Wang December 2022 China serves as a model for developing an online healthcare industry. From 2013 to 2019, the total value of China’s internet healthcare market grew from 4.5 billion CNY to 37.9 billion CNY. In November 2020, there were 54.8 million active users of internet health care, up from 46.9 million in November 2019 before the…
Continue reading “Working Paper 6: China’s Internet Health Market”
Working Paper 5: Assessing Quality of Care in India: Considerations for National Reform
Assessing Quality of Care in India: Considerations for National Reform By Anuska Kalita*, Liana Woskie*, and Winnie Yip *Joint First Authors December 2022 Even as the availability and affordability of healthcare improve, many countries are not experiencing anticipated gains in health outcomes. One potential driver for stagnating health outcomes is low-quality health services. For example, between 5.7 and 8.4 million deaths are estimated to result from poor-quality healthcare each year…
Publication: Comprehensive Assessment of Health System Performance in Odisha, India
India has recently implemented several major health care reforms at national and state levels, yet the nation continues to face significant challenges in achieving better health system performance. These challenges are particularly daunting in India’s poorer states, like Odisha. The first step toward overcoming these challenges is to understand their root causes. Toward this end, the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health conducted a comprehensive study in Odisha based…
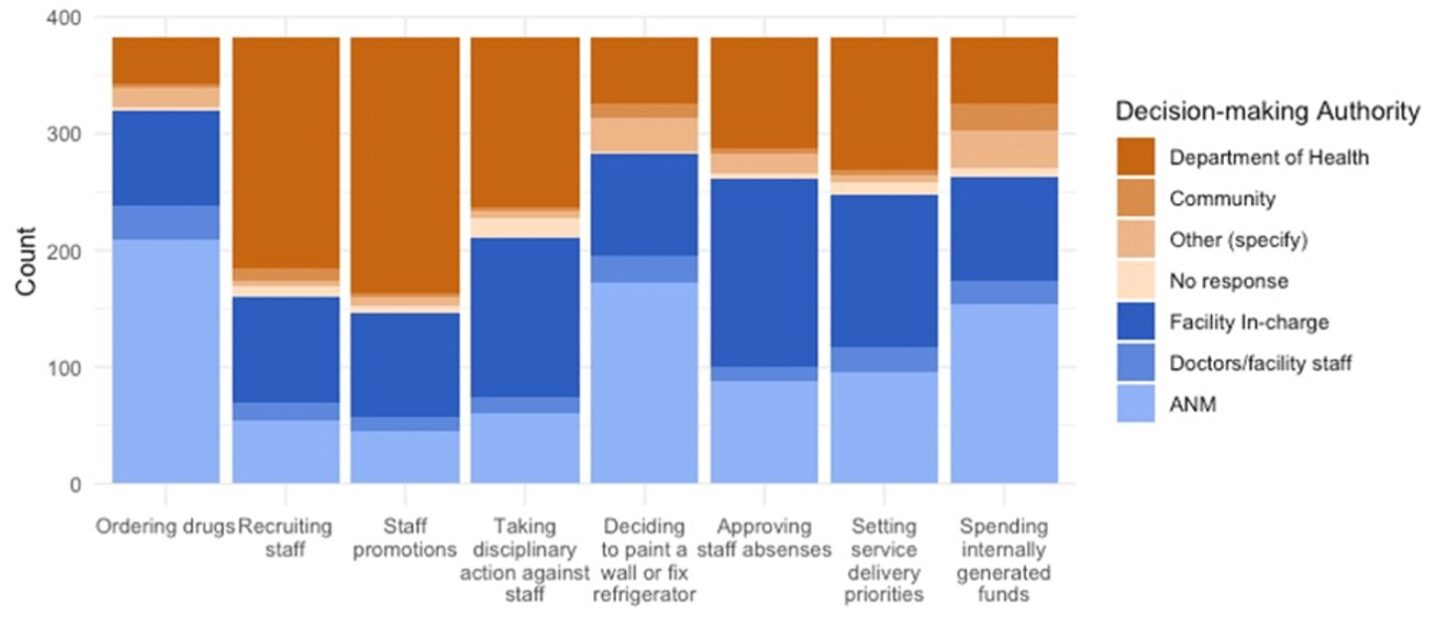
Publication: The relationship between decision-making autonomy and training on facility-level management performance of primary health care facilities in Odisha, India
Background Primary health care quality remains poor in many countries, despite its importance for universal health coverage. Evidence shows that better management of primary health care facilities improves service quality, and that facility managers’ autonomy and training levels can augment their management performance. In India, there is scant research in this area. Research questions include: 1) What is the effect of facility-level autonomy on management performance and is the effect…
Policy Implications from a State-Level Health System Assessment
Key Findings and Policy Implications from a State-Level Health System Assessment
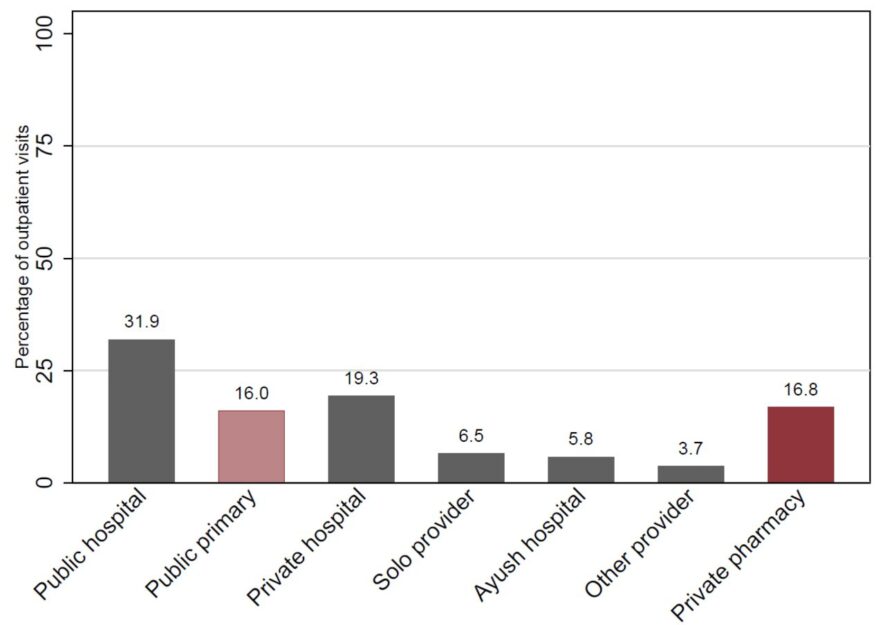
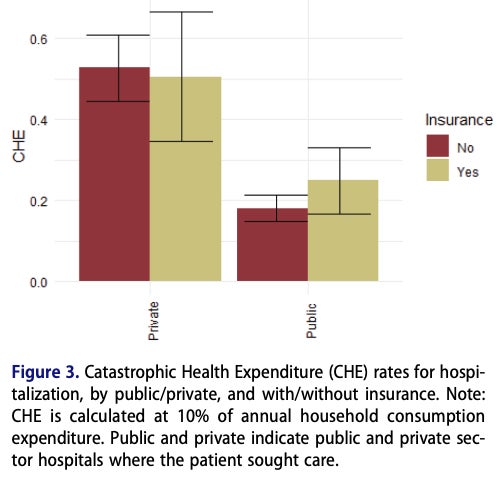
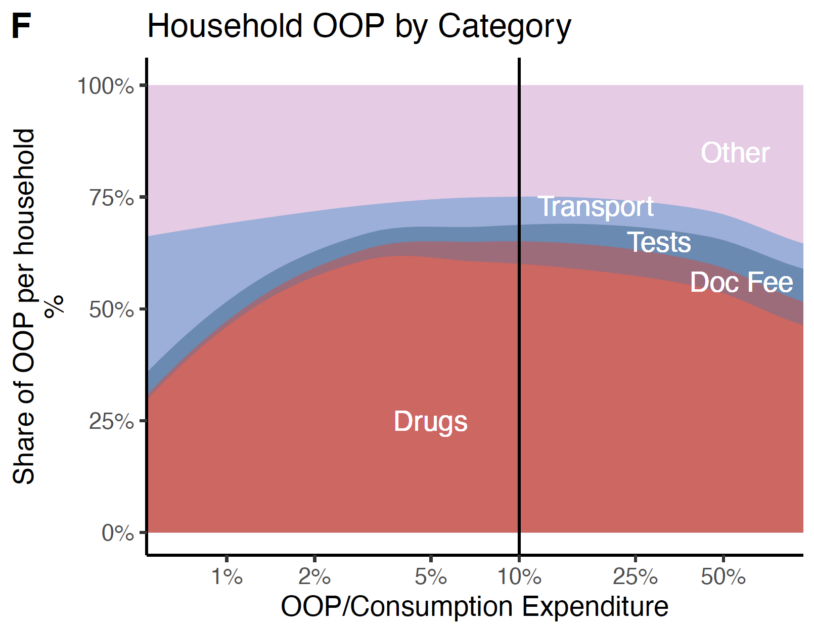
Publication: Catastrophic Health Expenditure on Private Sector Pharmaceuticals: A Cross-Sectional Analysis from the State of Odisha, India
Why does out of pocket expenditure remain high in India? We assess variation in financial risk protection in Odisha, India. Our novel study is the first to investigate the in-depth role of the private sector—especially private chemist shops—in providing outpatient care and also contributing to financial hardship due to healthcare costs. Introduction India has high rates of catastrophic health expenditure (CHE): 16% of Indian households incur CHE. To understand why…