Strategies for how local communities and states can reduce the risk of COVID-19 transmission during climate-related extreme events like heat waves, hurricanes, and wildfires.
Read nowAs COVID-19 cases continue to rise drastically across the U.S., and extreme weather events grip many parts of the country, this article in the New England Journal of Medicine calls on the federal government to provide more coordinated policy and funding given the inadequate and dangerous response to both crises in the U.S.
Lead author Dr. Renee Salas, our Climate MD leader and emergency physician, joined colleagues Dr. James Shultz from the University of Miami and Dr. Caren Solomon from Boston’s Brigham and Women’s Hospital to present both the challenges and solutions to address the disparate social and health impacts of this unprecedented time.
Challenges
-
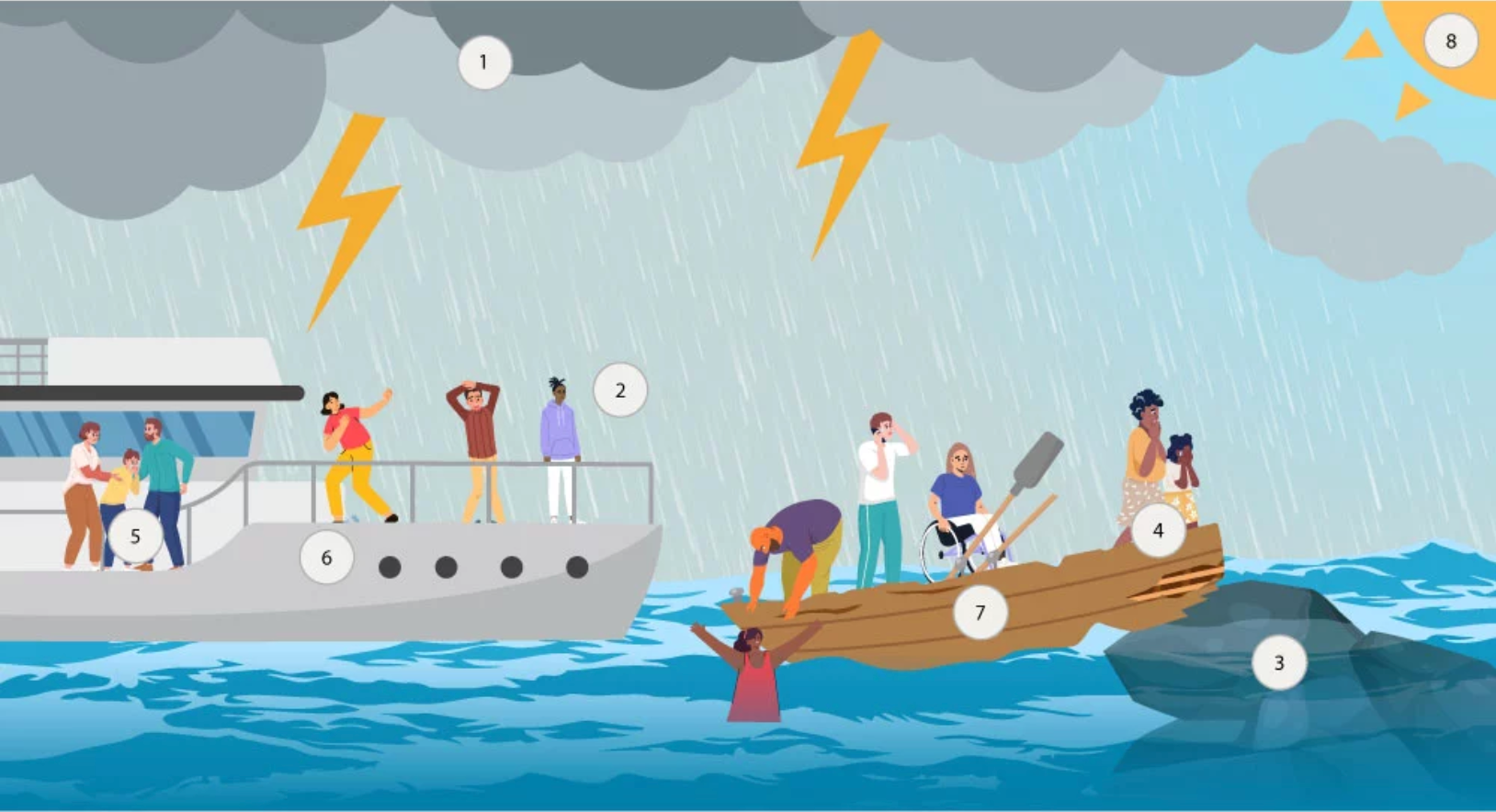
- Hurricanes and wildfires are predicted to be worse than average this year, which will force large groups of people to shelter or evacuate, increasing the risk of COVID-19 transmission.
- Heat waves, which have a high likelihood of making 2020 the hottest year on record, pose additional challenges by increasing the risk of heat-related illness for those wearing face masks and necessitating cooling centers to protect residents without air conditioning.
- Extreme weather events, made more frequent and intense by climate change, make it more difficult to maintain physical distancing, exacerbate coexisting conditions, and disrupt health care services, threatening efforts to contain transmission and improve outcomes of COVID-19.
- Extreme weather may damage hospitals and supply chains that make it more difficult for COVID-19 patients to access health care services.
Recommendations
With the lack of federal guidance, the authors recommend local and state agencies develop immediate short-term strategies on the key intersections between climate change and COVID-19 to protect the health of vulnerable and economically disadvantaged people, including those affected by structural racism, who are disproportionately harmed by the pandemic and the climate crisis. These include:
Short-term strategies
Extreme events (e.g., hurricanes, wildfires): evacuation and sheltering
-
- Communicate clearly to the public that the Covid-19 pandemic does not change the imperative to evacuate, given the substantial risks of remaining in place during extreme climate-driven hazards.
- Use existing community pandemic-communication channels to disseminate critical information.
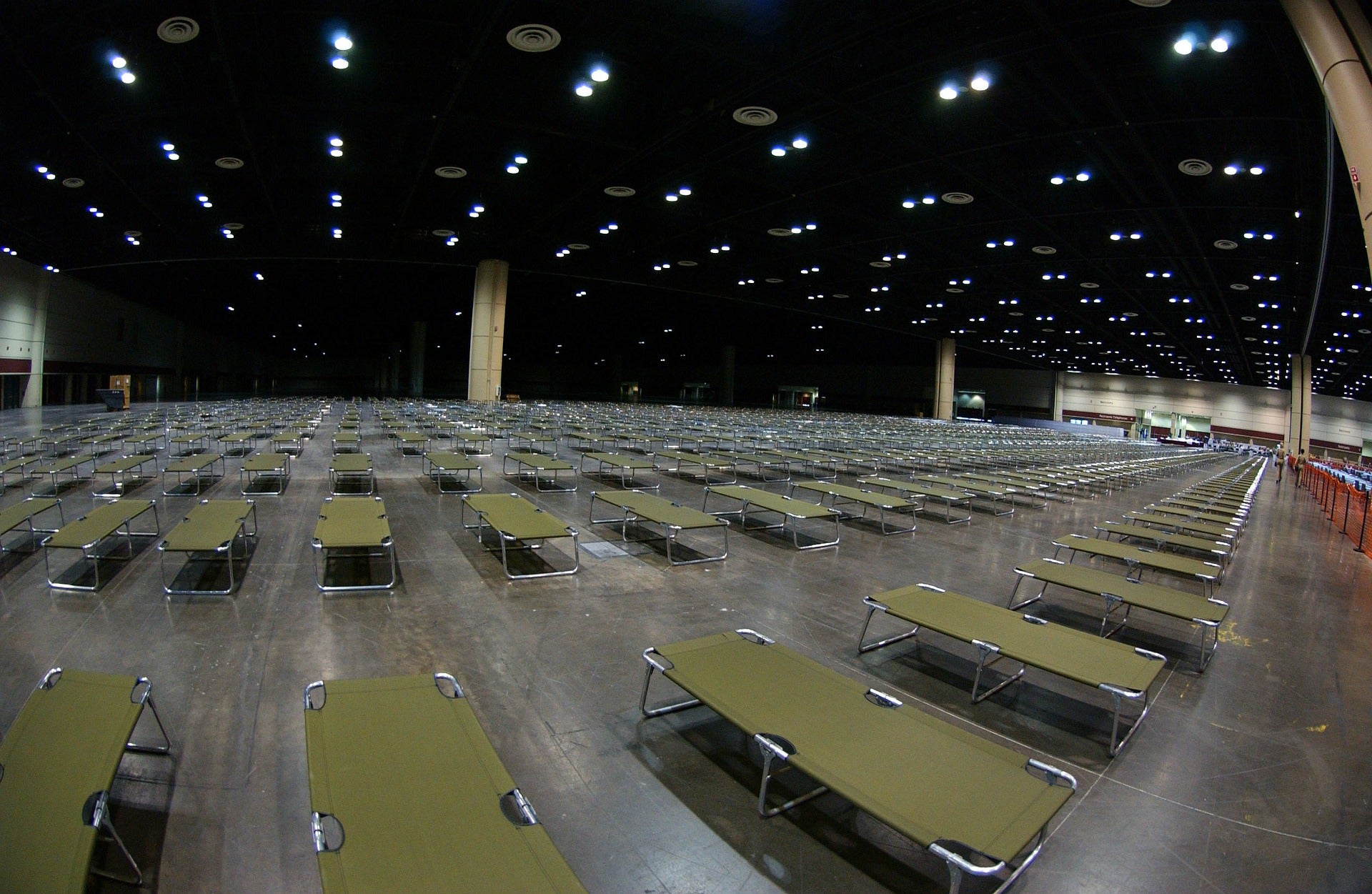
- Increase the number of available shelter sites, with lower occupancy per site, more separated spaces within sites, and more space per shelter resident (e.g., using smaller “noncongregate shelters,” hotels).
- Use standard shelter-registration information (name, contact phone number) for all persons entering, to facilitate contact tracing in case COVID-19 is diagnosed in persons who used the shelter.
- Implement shelter protocols for infection control, including daily symptom checks, isolation of symptomatic persons, mandatory wearing of face masks, ample supplies of hand sanitizer, hand-washing stations, and meals provided in disposable containers.
- Adapt guidance for minimizing COVID-19 viral transmission in mass care settings for use with in-home sheltering — because many evacuees shelter with family and friends.
Extreme heat: Remaining at home and cooling locations
-
- Provide electricity subsidies and extend moratoriums to prevent electricity and water shutoffs for people with pandemic-related unemployment and economic hardships to allow them to remain in their homes.
- Ensure effective alternatives to minimize heat exposure if designated cooling centers or popular indoor, air-conditioned venues are closed.
- Ensure that cooling centers follow guidelines similar to best-practice guidelines noted above.
- Minimize transmission risks by limiting occupancy and providing or requiring masks and hand sanitizer in air-conditioned venues open to the public, such as malls or movie theaters.
- Use phone text messages, as used for pandemic communication, for heat-health notifications.
Long-term strategies
-
- Prioritizing federal and state funding for mitigation plans to prepare for a future of climate-driven intensification of extreme weather, using an approach that takes all hazards into account.
- Strengthening our health care infrastructure and delivery systems, such as supply chains, are essential to ensuring resiliency during pandemic or climate shocks.
- Investing in health, clean air and water, and a stable climate in stimulus packages for recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic
- Creating sustained reductions in the use of fossil fuels can reduce the risks for multiple medical conditions—especially in vulnerable communities—by improving air quality and limiting the downstream health harms of the climate crisis.
- Tackling extreme heat by expanding green space, making more roofs white, and developing community outreach programs for the most vulnerable.
- Expanding the use of telemedicine in areas where computer or phone service is intact and the use of community paramedicine services to address medical and psychological needs