Photo by: Pixabay user Free-Photos
Producing and burning fossil fuels creates air pollution that harms our health and generates toxic emissions that drive climate change.
From the electricity that lights our homes to the cars we drive to work, modern life was built on fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. But burning them creates climate change and releases pollutants that lead to early death, heart attacks, respiratory disorders, stroke, asthma, and absenteeism at school and work. It has also been linked to autism spectrum disorder and Alzheimer’s disease.
Research from Harvard University, in collaboration with the University of Birmingham, the University of Leicester and University College London, found that more than 8 million people died in 2018 from fossil fuel pollution, significantly higher than previous research suggested—meaning that air pollution from burning fossil fuels like coal and diesel was responsible for about 1 in 5 deaths worldwide.
Each year, our team contributes to the Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change to track the impacts of climate change on human health across 44 indicators around the world. Our research analyzes the health impacts of burning fossil fuels and shows how much we have to gain by ending our reliance on them. Recent research from our Center:
- Identified at least 21 different hazardous air pollutants, as defined by the U.S. EPA, including benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylene, and hexane, in consumer-grade natural gas supplied to Massachusetts.
- Created a new inventory of air pollution impacts from stationary sources over the past decade that shows the negative impacts of burning natural gas and biomass have surpassed coal generation in many states, which is a trend that may continue.
- Conducted the first study to determine that Pennsylvania’s statewide setback regulations for fracking do not prevent setback incidents, and identified the potential risks and exposures for people living near fracking or underground natural gas wells.
- Showed that more people live closer to underground gas storage wells than previously thought. An estimated 20,000 homes and 53,000 people in predominantly suburban areas of PA, OH, WV, MI, NY, and CA live within a city block of active underground natural gas storage wells.
- Developed the science-based case for why it is “appropriate and necessary” for EPA to regulate mercury emissions from the power sector; and why the health benefits of regulation and remaining risks from mercury pollution in the U.S. should be assessed.


The 2022 Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change: Policy Brief for the U.S.
Climate change puts everyone at risk, but policy decisions and industry actions make some communities more vulnerable to the harms of climate change.

Home is Where the Pipeline Ends
Our study is the first to test for health-damaging air pollutants in unburned natural gas where it is used: in our homes.

2021 Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change: U.S. Policy Report
Our response to climate change must prioritize and optimize health and equity. We can improve health through climate actions that reduce our use of fossil fuels.
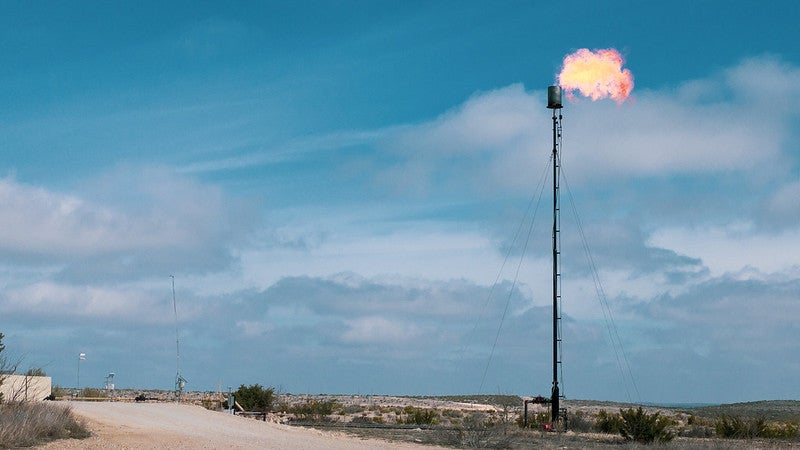

Methane Reductions in the Oil and Gas Sector can Protect Public Health
A literature review examines the last ten years of research on methane and health-damaging air pollutant emissions from the oil and gas industry.
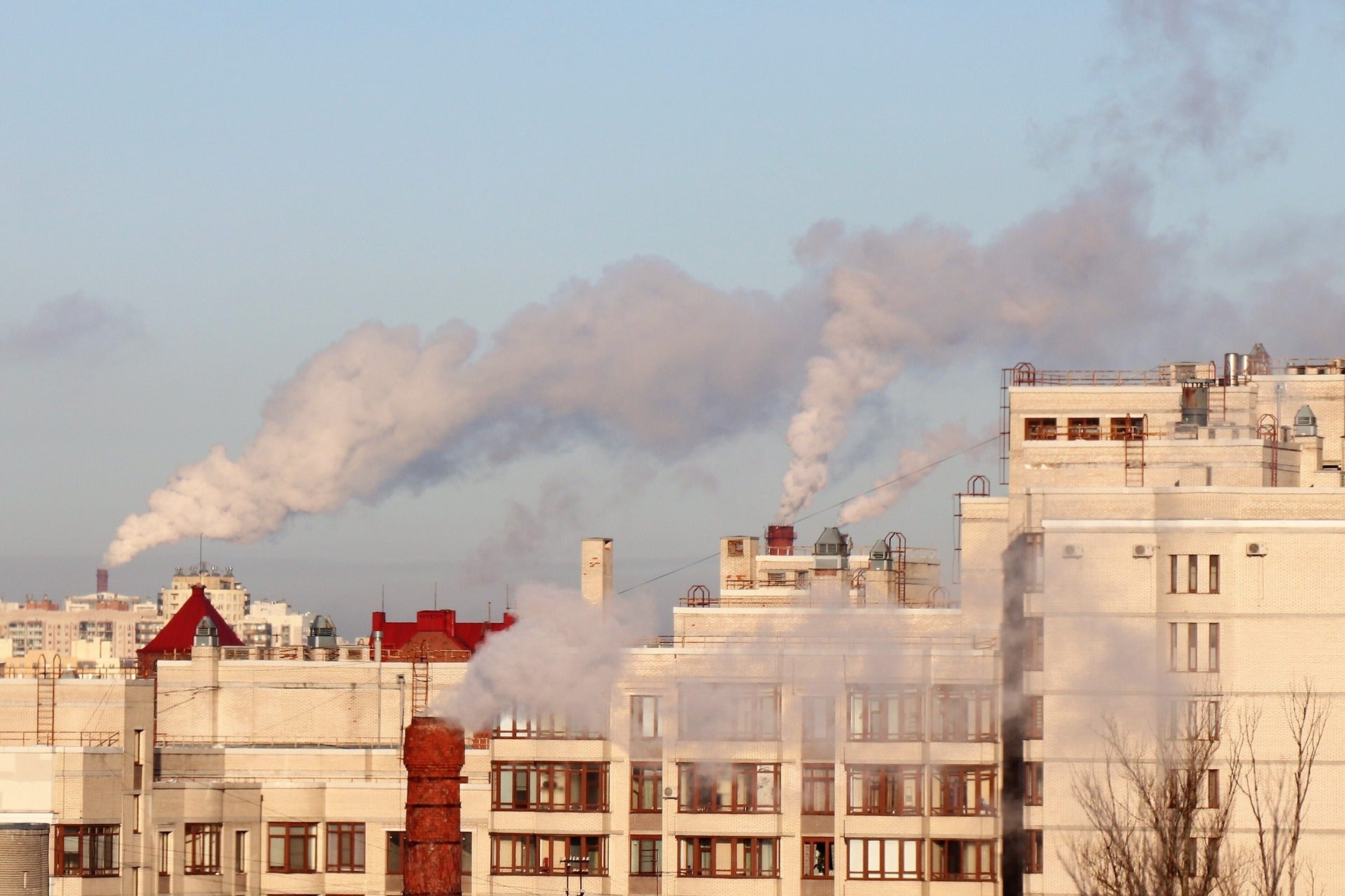

Negative impacts of burning natural gas and biomass have surpassed coal generation in many states
A new inventory of air pollution impacts from stationary sources over the past decade shows this trend may continue.
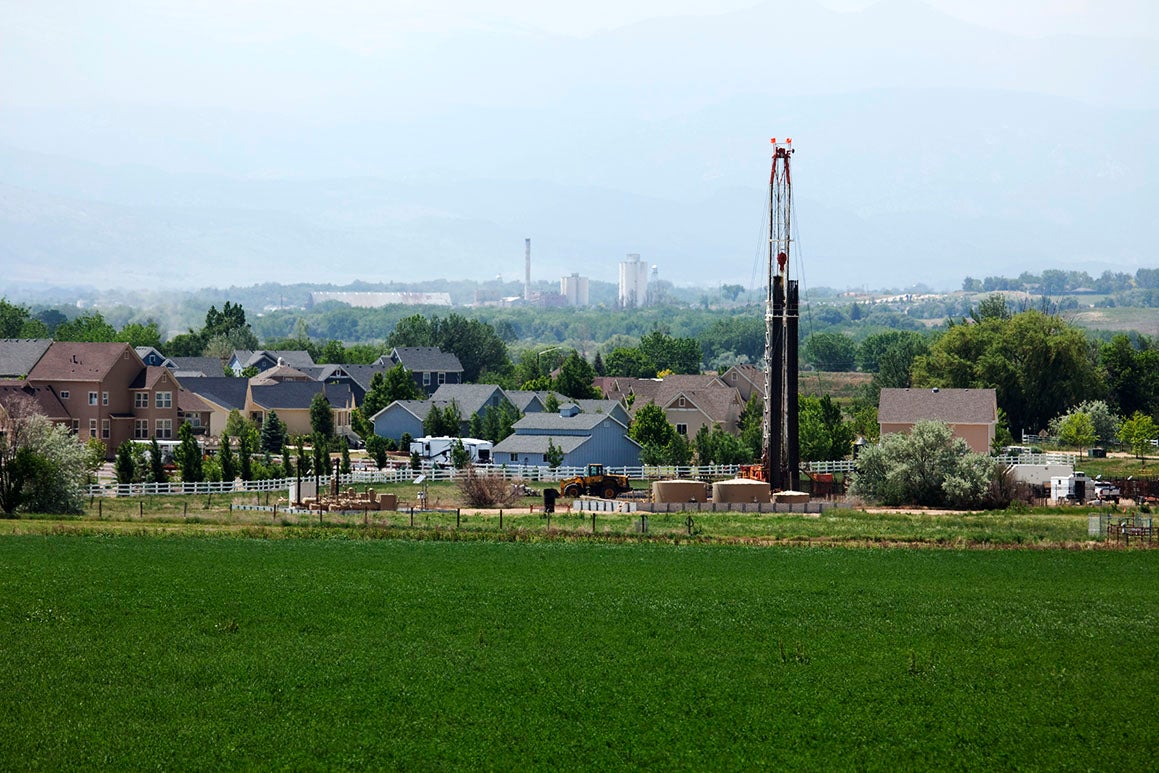

Pennsylvania setback regulations for fracking do not prevent setback incidents
The first study to look at the effectiveness of PA's statewide setback regulations and identify the potential risks and exposures for people living near fracking or UNG wells.
Pollution from fossil fuel combustion deadlier than previously thought
Fine particulate pollution from fossil fuel combustion was responsible for one in five early deaths worldwide in 2018, with vulnerable groups at greatest risk.

Fossil fuel air pollution responsible for 1 in 5 deaths worldwide
New research finds that deaths from fossil fuel emissions are higher than previously thought—more than 8 million people per year, worldwide.

'We Don't Have To Live This Way': Doctors Call For Climate Action
A sprawling analysis published by The Lancet focuses on public health data from 2019, and finds that heat waves, air pollution and extreme weather increasingly damage human health.

Natural Gas Is Now More Deadly Than Coal in 19 States
A new study found that using natural gas and biomass in sources like buildings and industrial boilers actually caused more deaths in 19 states as a result of air pollution than burning coal.

Natural gas and wood are replacing coal as the biggest pollutants
As coal recedes, other fuel sources are taking over as the biggest harms to public health.

Cleaner 'bridge' fuels are killing up to 46,000 Americans per year, study shows
Replacing coal with fuels like natural gas and wood may offer some climate benefits, but the harm to public health remains.

Harvard Chan School study shows negative impacts of burning natural gas and biomass have surpassed coal generation in many states
Burning natural gas, biomass, and wood now have more negative health impacts than burning coal in many states, and is a trend that may continue.
On Earth Day, US Power Brokers Acknowledge the Scale and Urgency of the Climate Crisis
Continued reliance on oil, gas, and especially coal is killing millions of people around the world every year, says our Director Dr. Aaron Bernstein.

Action Planet: Meeting the Climate Challenge
Our Director Dr. Aaron Bernstein joins Vice President Kamala Harris, Gina McCarthy, and others for a 1-hour Earth Day special, hosted by NowThis' Zinhle Essamuah.

5 things to know this Earth Day about how the environment affects health
To celebrate Earth Day, our Director Dr. Aaron Bernstein shares five things to know about the connection between the environment and our health.

The next Aliso Canyon could happen on L.A.’s Westside
Our Visiting Scientist Drew Michanowicz talks about his research into gas storage fields across six states to better understand the potential health consequences of leaks.

New Study: Pollution from Combustion of Fossil Fuel is More Dangerous Than Previously Imagined
Our Director Dr. Aaron Bernstein explains that individuals most at risk from fossil fuel pollution are those who can least afford it.

One in Five Deaths from Fossil Fuels
Our Director Dr. Aaron Bernstein joins Host Steve Curwood to discuss the implications of new research showing fossil fuel pollution is responsible for one in five early deaths worldwide.
