Symposium highlights lesser-known members of the microbiome
Lesser-studied members of the microbiome, including viruses and fungi, were the focus of the fifth annual symposium of the Harvard Chan Microbiome in Public Health Center, held May 15 at Harvard Medical School’s Joseph B. Martin Center.

Science fueled by social justice
Sydney Stanley, PhD ’23, researches infectious diseases with an eye toward improving the health of the world’s most vulnerable populations

Report makes the case for new TB vaccines
Investing more financial resources to accelerate scientific progress toward an effective tuberculosis vaccine will save lives, fight antimicrobial resistance, advance health equity, improve economic growth, and bring a substantial return on investment, according to a new report.
Is new malaria vaccine ‘world-changing’? Maybe.
Harvard Chan School's Dyann Wirth offers some thoughts on a new malaria vaccine and its potential impact.

Dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapies for HIV-1 effective in pregnancy
Dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapies for HIV-1 are more effective for pregnant people than some other ART regimens commonly used in the U.S. and Europe, according to a new Harvard Chan School study.

A better antibiotic for tuberculosis treatment
PhD candidate Harim Won is developing a new type of antibiotic to address long-standing issues of lengthy treatments and drug resistance, using a new approach to turn a normal protein system in the bacterial cell against itself.
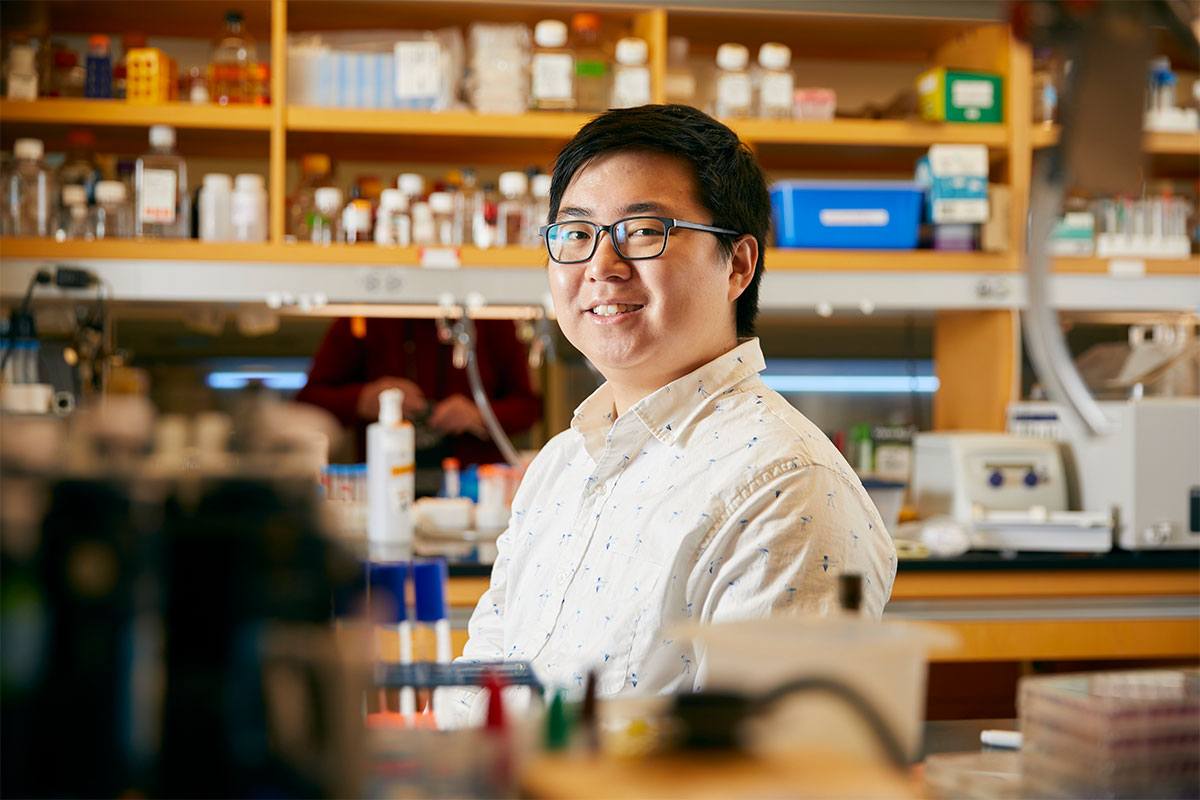

‘The infectious disease that nobody ever thinks about’
To mark World TB Day, March 24, Harvard Chan School's Sarah Fortune, a TB expert, discusses the state of the disease worldwide, obstacles to fighting it, and the latest research.
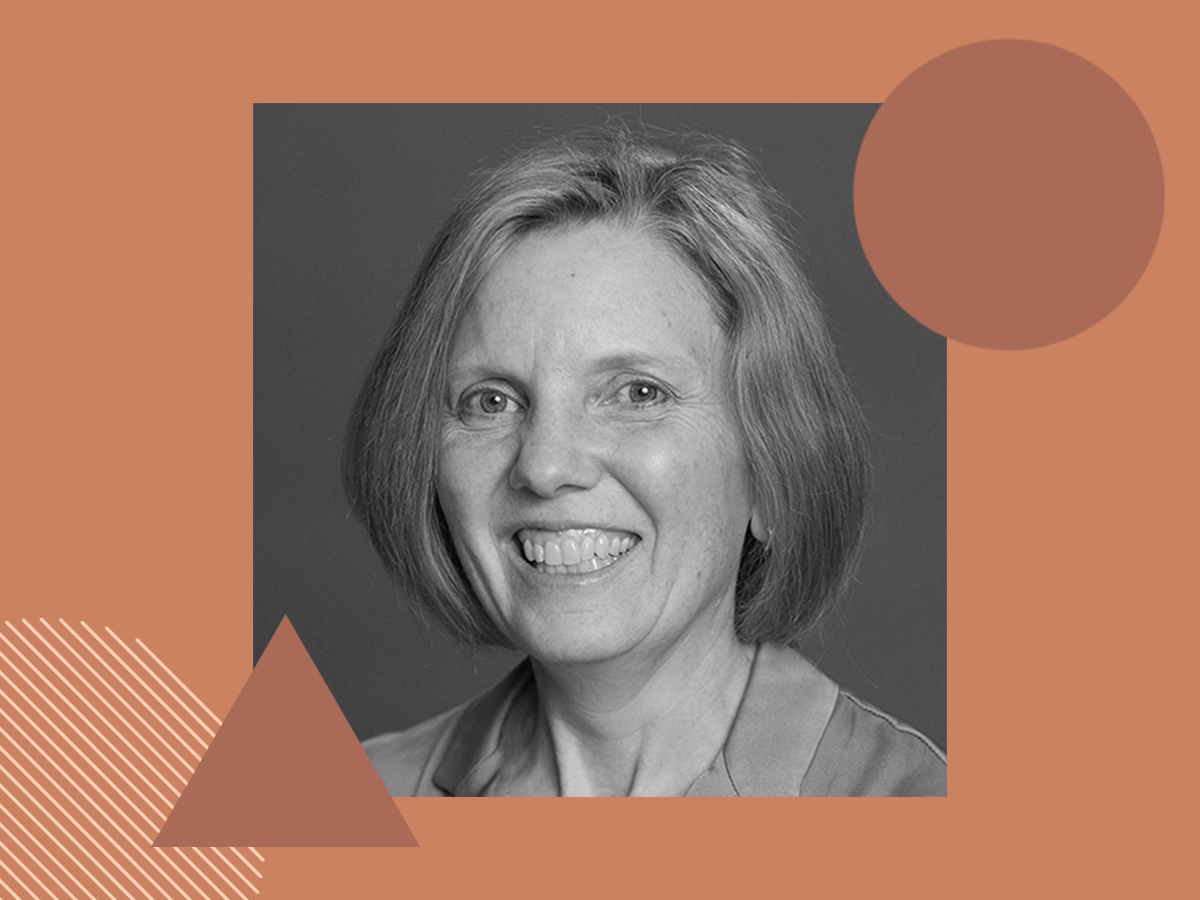

Threat of antibiotic resistance looms large
While COVID-19 has garnered significant attention from the public and media, antibiotic resistance is a slow-moving threat to global health that is often overlooked even though the World Health Organization estimates that antibiotic-resistant infections could kill as many…
Climate in the clinic
Climate change—and how it affects health—should be front and center for doctors, health care workers, and hospitals, said speakers at a symposium.

Excessive rates of antibiotic prescriptions for children in low- and middle-income countries
Children in low- and middle-income countries are receiving an average of 25 antibiotic prescriptions during their first five years of life.