The Quantitative Biomedical Research Center (QBRC) at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health under the Department of Biostatistics supports the biomedical research community. QBRC provides large scale biomedical data mining, management, pattern recognition, and research software engineering (RSE) support to scientists in the Harvard research community and beyond.
 Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
655 Huntington Ave
Building 2, Room 410
Boston, MA. 02115-6009
qbrc@hsph.harvard.edu
Researchers can work with the qBRC by either fee-for-service consulting projects, online analysis platform, or through research grants. The QBRC provides data analysis and data mining services for -omic and high dimensional data sets using bioinformatics, systems biology, and machine learning techniques. The QBRC staff will assist investigators on planning, analyzing, and interpreting the resulting data and provide publication ready materials. We are particularly equipped to analyze “Big Data” and to implement complex algorithms using secure Cloud Computing infrastructure. The QBRC also provides research software engineering (RSE) services.
We provide the following four types of services:
Data Mining
Pattern Classification
We offer highly customized data mining services using machine learning tools such as regression models, unsupervised clustering methods, and supervised learning methods. These type of projects include but not limited to:
- Population subtype discovery
- Biomarker discovery
- Predictive model construction
Multi-Data Type Integration
Technology advancements have made it cost-effective to collect diverse types of high dimensional data. We offer network-based computational methods to combine multiple data types, such as clinical, questionnaires, image, and genomic data, for a set of samples to perform pattern recognition and model interactions.
- Identify sample similarity and community from multi-type data measurements
- Assess level of interaction between driver and respondents (i.e. gene expression driven by transcription factor binding)
- Isolate single sample contribution to network
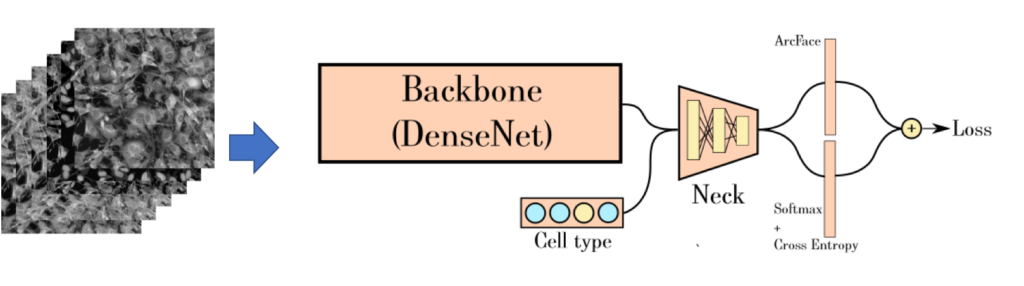
Image Analysis using Deep Learning
Complex deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which are able “automatically” to capture predictive features in image data once appropriately trained, have garnered significant attention for their potential utility in biomedical applications with its accuracy. We provide deep learning neural network model construction service for quantitative image analysis. We currently support high-throughput microscopy assays using state-of-the-art convolution neural networks (CNNs) and related techniques for model construction.
Genomic Data Analysis
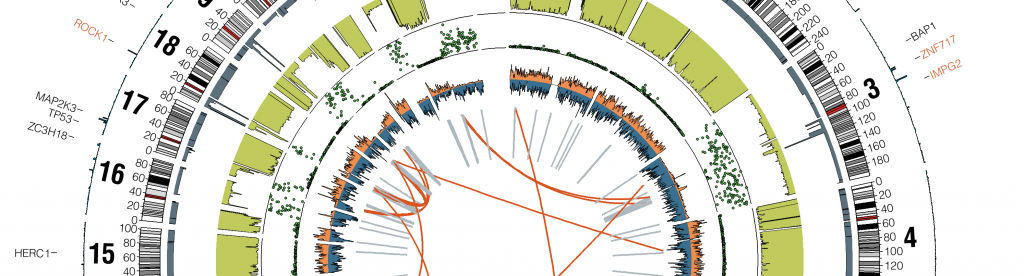
We offers a wide range of easy-to-use standard Next Generation Sequence data analysis pipelines that can rapidly process large number of samples (>100) from raw files, analyses include:
- Germline/Somatic Mutation Analysis
- Single Cell RNA-Seq Analysis
- Bulk RNA-Seq
- Small RNA-Seq
- ChIP-Seq
Research Software Engineering
Do you need help with software or cloud engineering tasks that distract you from doing science? We can accelerate your research by developing usable, robust, and maintainable scientific software, and more!
We can assist with:
-
- Software design, implementation, optimization, refactoring, and maintenance
- Every phase of the research software engineering life cycle from pre-publication to post-publication
- Cloud computing
- From budgeting for grant applications to implementing, securing, and maintaining infrastructure as code
- Data management
- Storage and sharing of large ‘omics data sets
- Data visualization
- interactive dashboards using R Shiny and other tools
- Software package management
- Containers or Conda packages for your software tools to facilitate distribution
- Many other areas of scientific computing
- HPC, web development, etc.
- Software design, implementation, optimization, refactoring, and maintenance
We have over 30 years of combined professional research software engineering experience. Our knowledge of the research life cycle allows us to adapt software engineering best practices into workflows to support sustainable software for research.
Work with us
Acknowledgments and authorship
The QBRC does not require co-authorship on studies using data generated solely on a fee-for-service basis using standard analysis methods by qBRC staff. In cases where significant intellectual contributions have been made by qBRC staff, co-authorship may be appropriate, following usually-accepted scientific practice. The requesting researcher and qBRC Director will discuss appropriate authorship.
Please note that payment of fees for data analysis services and authorship are not mutually exclusive and that authorship does not substitute for payment of Center expenses for services rendered.
Costs
qBRC consulting for data analysis and software development is charged by hourly rate. The rates are $182 for HU/HMS/HSPH members, $200 for other non-profits institutes, and $227 for industry members.
For more information, email us at qbrc@hsph.harvard.edu.



