Introduction
This report underscores a critical trend among G20+ nations grappling with increasing healthcare costs and inequities in access and outcomes. The overarching goal is to evolve their healthcare systems to provide ‘value for money and value for many’ by focusing on efficiency, effectiveness, equity, and responsiveness. Although efforts have been initiated at various levels, no large-scale population-level impact has been observed so far. Harvard University’s Health Systems Innovation Lab (HSIL) has developed a High-Value Health System Model (HVHS) consisting of 10 components that cover digital data systems, analytics, cost, and outcomes measurement systems, benchmarking, integrated care pathways, value-based payment and procurement models, integrated provider networks, and strategic change and innovation ecosystems. However, the study notes that while all countries have implemented some components, none have fully integrated all aspects to achieve a complete HVHS transition.
The report applies the HSIL framework to gauge G20+ nations’ progress towards the HVHS transition, using expert surveys, interviews, and desk research. Although progress has been made, the extent of implementation varies significantly among countries. The most significant improvement was seen in digital data systems and strategic change initiatives, while moderate progress was noted in analytics and cost and measurement systems. The components related to value-based payment models and value-based procurement were identified as areas needing accelerated progress. While most nations have established health data ownership and usage policies and are using digital data systems extensively, there is scope to increase the use of existing data systems and analytics to enhance policy and practice. However, less than half of the countries have established performance datasets allowing regional or provider comparisons. Slow progress in aligning financial incentives and setting up regular cost and outcome measurement systems was also noted. Despite these challenges, the report highlights successful initiatives that could serve as models for countries seeking to expedite their HVHS transition.

Download the report
The Harvard High-Value Health System Components
Conceptual Model
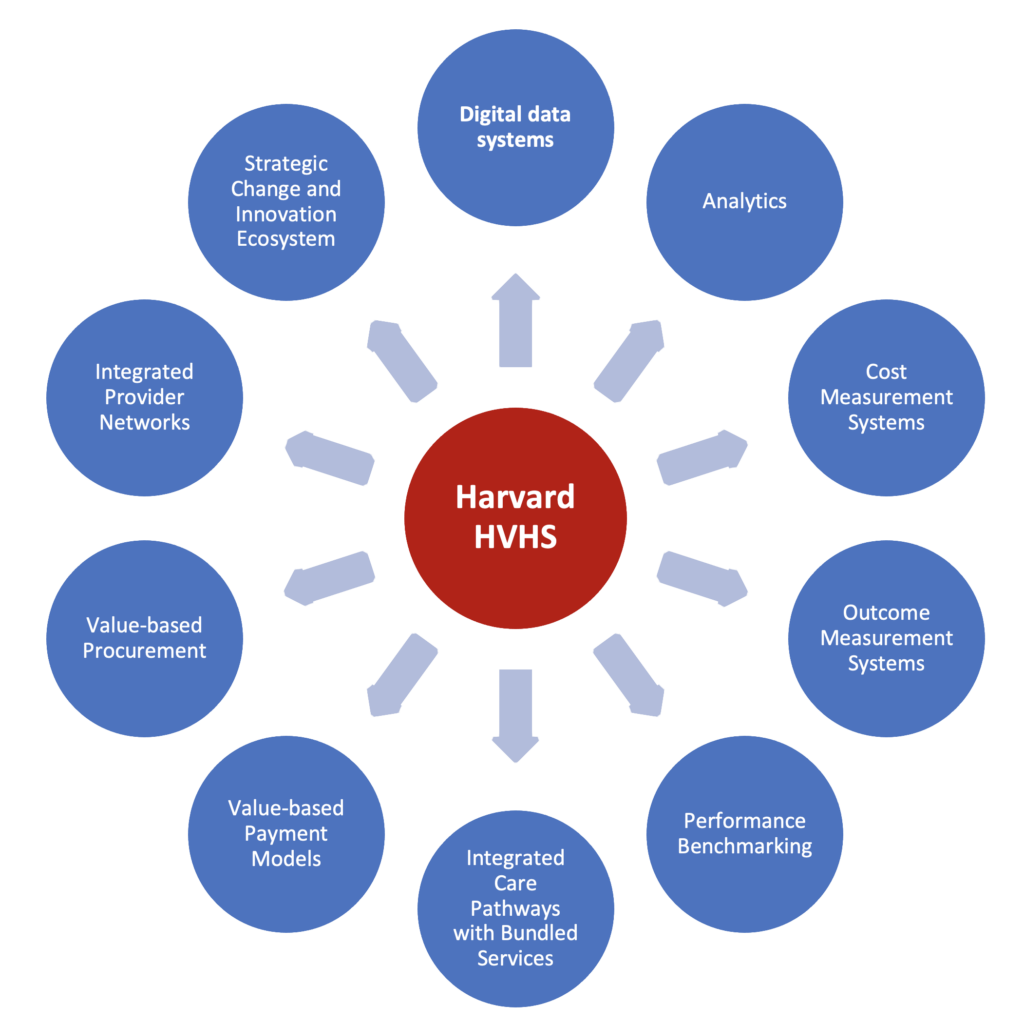
This study is underpinned by the Harvard High-Value Health Systems Model (HVHS). The Harvard HVHS model consists of 10 interdependent and mutually reinforcing design components (Figure 1) that characterize the ongoing transition in health systems towards a ‘value’ predominant system orientation. The HVHS model is detailed in Building a High-Value Health System, Transition to Health Systems: A Primer and a position paper on Rethinking Health System Design: Towards a High-Value Health System Model.
The conceptual model builds on and represents an evolution of several critical HSIL frameworks, notably the HSIL Health System Framework and HSIL Complex Healthcare Innovation Framework – both of which have been used to examine health system performance and analyze the adoption and diffusion of innovations in health systems and have been applied in more than 30 countries. This prior knowledge and empirical evidence have helped to understand better how health systems behave in different countries, the major forces that influence their performance, and the policies, programs, institutional arrangements, and interventions designed to enhance system performance and ultimately inform the Harvard HVHS model.
This report has been created in collaboration with the G20 Global Innovation Hub for Improving Value in Health (https://www.g20hub.org/).
An Introduction to High-Value Health Systems
As part of the Hub Innovation Series, Ebele Anidi was in conversation with Professor Rifat Atun, Dr. Che Reddy, and Johnattan Garcia Ruiz from the Health Systems Innovation Lab.
In this episode, they present the findings from the collaborative study between Harvard and the Global Innovation Hub. The team discusses a new framework to examine G20+ countries’ progress in transitioning to a high-value health system model. They highlight essential components and supportive conditions for this transition, emphasizing the need for digital data systems, analytics, cost and outcome measurement, integrated care pathways, value-based payment models, integrated provider networks, strategic change, and innovation.
The episode can be found at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UdfAIzhnxDU&list=TLGG6EIzdyhk1MgyODEwMjAyMw&t=274s.




