An emerging central upstream regulator of the response to dietary restriction is the pro-longevity AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a cellular energy sensor that is activated during energy stress. AMPK is a central node for many critical nutrient responsive pathways that have been linked to longevity (see figure). One focus of our lab is identifying the longevity-specific processes regulated by AMPK, using a combination of genetic and molecular approaches in both the nematode worm C. elegans and mammalian cell culture.
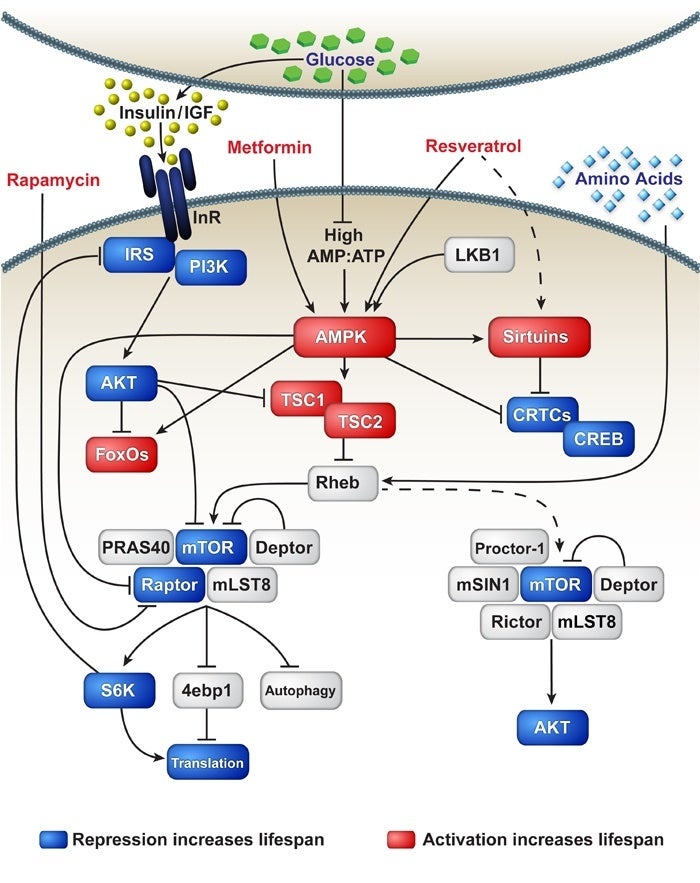
Using C. elegans as a model system we have demonstrated that an essential downstream mechanism linking AMPK to longevity is the transcriptional cofactor CRTC-1. This work established a novel aging role for CRTCs, which are known in mammals to be critically linked to age-onset pathologies such as obesity, diabetes and neurodegeneration. This finding was contrary to perceived but unproven expectations that AMPK activation promotes healthy aging via effects on the mTOR complex 1. In addition we have worked in a collaboration to demonstrate a novel in interaction between AMPK and HIF1-1 in reactive oxygen species (ROS) based hormesis and longevity. Recently we have shown that targeting perception of energy intake rather than energy levels themselves can lead to beneficial effects on healthy aging; the positive effects of AMPK on longevity and mitochondrial dynamics/metabolism are mediated cell-nonautonomously via CRTC-1 in neurons and s resulting catecholamine signal. This work also demonstrated that the positive effects of AMPK on aging can be molecularly uncoupled from detrimental pleiotropic effects on physiology by neural CRTC-1. This is a key finding as we search for new targets to recapitulate the beneficial effects of DR on health.
- Egan DF, Shackelford DB, Mihaylova MM, Gelino S, Kohnz RA, Mair W, Vasquez DS, Joshi A, Gwinn DM, Taylor R, Asara JM, Fitzpatrick J, Dillin A, Viollet B, Kundu M, Hansen M, Shaw RJ. Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Science. 2011 Jan 28;331(6016):456-61. PubMed PMID: 21205641; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3030664.
- Mair W, Morantte I, Rodrigues AP, Manning G, Montminy M, Shaw RJ, Dillin A. Lifespan extension induced by AMPK and calcineurin is mediated by CRTC-1 and CREB. Nature. 2011 Feb 17;470(7334):404-8. PubMed PMID: 21331044; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3098900.
- Hwang AB, Ryu EA, Artan M, Chang HW, Kabir MH, Nam HJ, Lee D, Yang JS, Kim S, Mair WB, Lee C, Lee SS, Lee SJ. Feedback regulation via AMPK and HIF-1 mediates ROS-dependent longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Oct 21;111(42):E4458-67. PubMed PMID: 25288734; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4210294.
- Burkewitz K, Morantte I, Weir HJ, Yeo R, Zhang Y, Huynh FK, Ilkayeva OR, Hirschey MD, Grant AR, Mair WB. Neuronal CRTC-1 governs systemic mitochondrial metabolism and lifespan via a catecholamine signal. Cell. 2015 Feb 26;160(5):842-55. PubMed PMID: 25723162; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4392909.



