Related Topics
A wide-angle view of global health
Humanity has made huge achievements in health, but has a long way to go. That’s the message in an article by Harvard School of Public Health’s David Bloom in the December 2014 issue of Finance & Development (F&D)—the…
Premature deaths could be reduced by 40%
The number of premature deaths worldwide could be reduced by 40% by 2030 with political commitment and sustained international efforts, according to a new study in The Lancet. The study suggests that half of all deaths under age…
Heart Disease
Jump to: –What is heart disease? –Types –Risk factors --Calculating risk –Prevention is possible Definition and Overview “Heart disease,” often used interchangeably with the term “cardiovascular disease” (CVD), describes several conditions affecting the heart, the blood vessels that nourish…

Disease Prevention
Chronic diseases —including heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and cancer— account for some of the most common health problems in the United States, according to statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Yet many of these…
Newly discovered mechanism suggests novel approach to prevent type 1 diabetes
Experimental findings could lead to new, inexpensive therapy using a naturally occurring bile acid For immediate release: Wednesday, November 13, 2013 Boston, MA – New research led by Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) demonstrates a disease mechanism…
Symposium explores trends in cardiovascular disease in Brazil, Mexico
November 8, 2013 —The rise of cardiovascular disease in two rapidly growing countries—Mexico and Brazil—was the focus of a symposium organized by Swiss Re and Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) on October 15-16, 2013 at the American…

The staggering toll of noncommunicable diseases
October 29, 2013 — Chronic diseases including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer, are the leading cause of death worldwide, with the burden falling heaviest in low- and middle-income countries. A new article by Harvard School of Public Health…
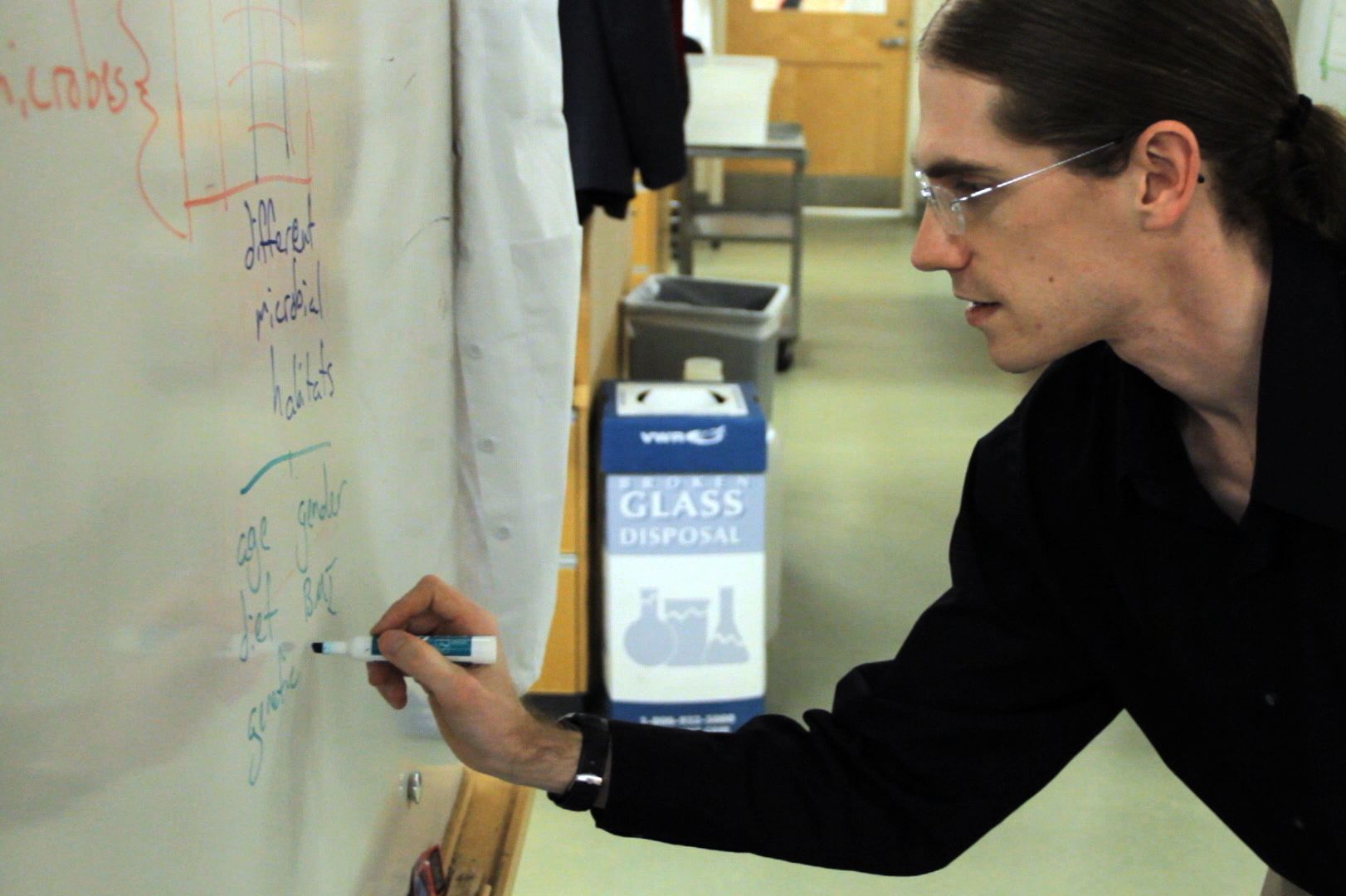
Our bugs, ourselves
[ Spring 2013 ] Microbes in and on our bodies outnumber human cells 10 to 1—and may determine how we get sick and stay well. The story of public health has largely been a story of conquering infections,…

Survey finds public support for legal interventions to fight obesity, noncommunicable diseases
For immediate release: Monday, March 4, 2013 Boston, MA — The public is very supportive of government action aimed at changing lifestyle choices that can lead to obesity, diabetes, and other noncommunicable diseases—but they’re less likely to support…

Human Microbiome Project: Analyzing microbes that play a role in health and disease
February 2013 — Curtis Huttenhower, assistant professor of computational biology and bioinformatics, talks about the Human Microbiome Project and the role that microbes—organisms like bacteria, viruses, and fungi that live in the stomach, in the mouth, on the skin,…
