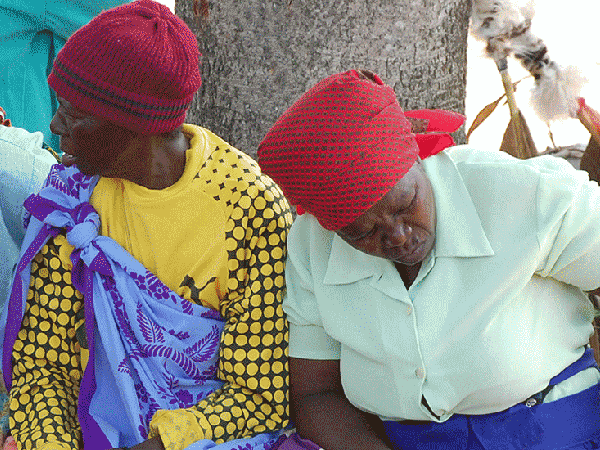Scientists affiliated with Health and Aging in Africa: A Longitudinal Study in South Africa (HAALSI) have found that telomere length is associated with health and aging biomarkers (e.g., age, mortality, blood pressure) in much the same way that they are associated with these biomarkers in more frequently studied high-income countries.
Diagnosing dementia in rural South Africa using online consensus; cash transfers at earlier age in South Africa to support cognitive health later on; paving the way with promise for genomic studies on cognition in Africa
Three studies by HAALSI researchers based on a rapidly aging population in rural South Africa are contributing to the much-needed scientific literature on global cognitive aging. A study published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring found that a multidisciplinary, web-based consensus conference approach for diagnosing cognitive impairment and dementia in rural South Africa was feasible, and identified the key factors responsible for diagnostic variability among raters. In…
HAALSI study finds improvement in hypertension control in aging South African population
Researchers affiliated with the Health and Aging in Africa: A Longitudinal Study of an INDEPTH Community in South Africa (HAALSI) project have published a study on an aging population in rural South Africa in which more than half suffer from hypertension. Findings reveal that there have been improvements in addressing the condition in every phase of the treatment “cascade” (i.e., awareness, treatment and control).
Older adults in rural South Africa who care for their grandchildren may also be safeguarding their cognitive function
Three researchers (Harvard Pop Center Research Scientist Elyse Jennings, Research Associate Director Meagan Farrell, and former Bell Fellow Lindsay Kobayashi) affiliated with one of the flagship projects at the Harvard Pop Center — Health and Aging in Africa: A Longitudinal Study of an INDEPTH Community in South Africa (HAALSI) — have published their findings in the Journal of Aging and Health.
Assessing the scale for assessing depression in rural South Africa
Researchers from the Harvard Pop Center in Cambridge, MA and the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, South Africa who are affiliated with the HAALSI study have published a paper in the Journal of Affective Disorders that finds that the reliability of the commonly used scale to assess depression (Center for Epidemiologic Depression Scale (CES-D)) differed by gender. Authors of the study include: Leslie B. Adams, Meagan Farrell, Sumaya Mall,…
Continue reading “Assessing the scale for assessing depression in rural South Africa”
A hopeful discovery about later-life cognitive function in those exposed to early-life adversity in rural South Africa
The HAALSI team of researchers is one of the first to look at the impacts of early-life adversity (such as parental unemployment, discord and substance abuse, and physical abuse) on later-life cognitive function in rural South Africa. Their findings published in Psychology and Aging suggest that cognitive function is, for the most part, resilient against early-life adversity.